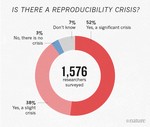
Projects

Automated Image Analysis
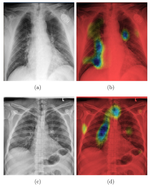
AI-assisted diagnosis in rheumatology

Human Reproduction Reloaded
We are proud to be part of the UZH University Research Priority Programs (URPP) where we together with the Schwank lab investigate the …
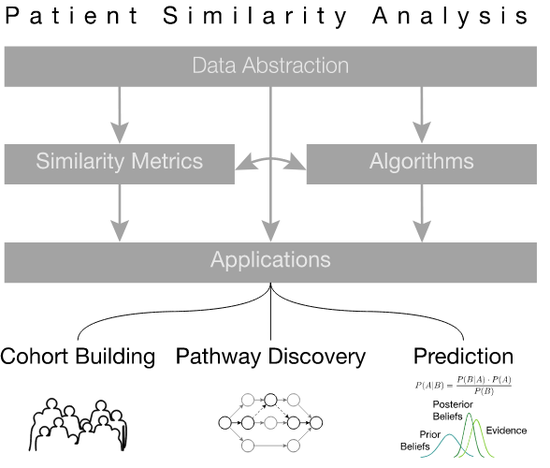
Patient Similarity Analysis
Since the early days of computing, healthcare professionals have dreamt of using the vast storage and processing powers of computers to …
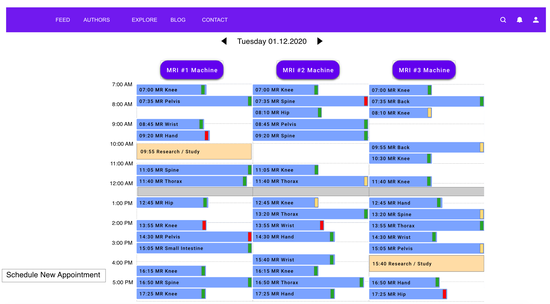
MRIdle
Helping reduce idle time in the USZ Radiology department